kpss test in r package|how to test for stationarity : chain store This function computes the Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin test statistic for examining the null hypothesis that a given series is level-stationary, or stationary around a deterministic trend .
Resultado da 17 de ago. de 2022 · Vazados de famosas. 17 de agosto de 2022 Por. Muito se tem escrito sobre vazados de famosas. Cada vez há mais Brasileiros que utilizam o Telegram como ferramenta de comunicação para encontros, grupos de sexo, informação, etc. Toda as pessoas querem saber mais .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 26 de jan. de 2024 · Poppy Playtime Chapter 3 Grab Pack V2.0 3D Model. Something went wrong with the 3D viewer. Learn how to fix it here.
Computes the Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin (KPSS) test for the null hypothesis that x is level or trend stationary. To perform a KPSS (Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin) test in R, we can use the urca package. This package provides functions to conduct unit root tests, including the KPSS test. Prepare your time series data. Ensure that . The KPSS test in R can be performed using the kpss.test() function from the tseries package. This function calculates the KPSS test statistic and compares it to the critical values .Performs Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin (KPSS) test for the null hypothesis that x is a stationary univariate time series.
To perform a KPSS test in R, you need to first install the tseries package. Then, you can use the kpss.test() function to run the KPSS test. This function takes in a time series as its argument and returns the test statistic, p .This function computes the Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin test statistic for examining the null hypothesis that a given series is level-stationary, or stationary around a deterministic trend .
To perform the KPSS test in R, we can use the “ur.kpss” function from the “urca” package. The function takes as input a time series and returns the test statistic along with its p .
Two statistical tests would be used to check the stationarity of a time series – Augmented Dickey Fuller (“ADF”) test and Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin (“KPSS”) test. A method to convert a non-stationary time series into . The problem with R is that there are several packages that can be used for unit root tests. Just to mention another one, > library (tseries) > adf.test (X,k=0) Augmented Dickey .Performs the Augmented Dickey-Fuller test for the null hypothesis of a unit root of a univarate time series x (equivalently, x is a non-stationary time series). Rdocumentation. powered by. Learn R Programming. aTSA (version 3.1.2.1) Description. Usage Value, , . How to Implement the KPSS Test? In python, the statsmodel package provides a convenient implementation of the KPSS test. A key difference from the ADF test is the null hypothesis of the KPSS test is that the .
Performs stationary test for a univariate time series. Rdocumentation. powered by. Learn R Programming. aTSA (version 3.1.2.1) Description. Usage Value, , Arguments. Author. Details, . . method = "kpss") # same as kpss.test(x) Run the code above in your browser using .Hence, this test reduces to simply test the hypothesis that \{ \xi_t \} is stationary, that is, H_0: \sigma^2_z = 0. The test statistic combines the one–sided Lagrange multiplier (LM) statistic and the locally best invariant (LBI) test statistic (Nabeya and Tanaka, (1988)). KPSS test; Here, in the KPSS testing procedure, two models can be considerd : with a drift, or with a linear trend. Here, the null hypothesis is that the series is stationnary. . One more time, it is possible to use another package to get the same test (but again, a different output) > kpss.test(X,"Level") KPSS Test for Level Stationarity . Performs the KPSS unit root test, where the Null hypothesis is stationarity. The test types specify as deterministic component either a constant "mu" or a constant with linear trend "tau". . R Package Documentation. rdrr.io home R language documentation Run R code online. Browse R Packages.
x <- rnorm(1000) # is level stationary kpss.test(x) y <- cumsum(x) # has unit root kpss.test(y) x <- 0.3*(1:1000)+rnorm(1000) # is trend stationary kpss.test(x, null = "Trend") [Package tseries version 0.10-56 Index ]
jarque.bera.test: Jarque-Bera Test; kpss.test: KPSS Test for Stationarity; maxdrawdown: Maximum Drawdown or Maximum Loss; na.remove: NA Handling Routines for Time Series; NelPlo: Nelson-Plosser Macroeconomic Time Series; nino: Sea Surface Temperature (SST) Nino 3 and Nino 3.4 Indices; plotOHLC: Plot Open-High-Low-Close Bar Chart KPSS test is a statistical test to check for stationarity of a series around a deterministic trend. Like ADF test, the KPSS test is also commonly used to analyse the stationarity of a series. However, it has couple of key differences compared to the ADF test in function and in practical usage. Therefore, is not safe to just use them interchangeably. We'll . jarque.bera.test: Jarque-Bera Test; kpss.test: KPSS Test for Stationarity; maxdrawdown: Maximum Drawdown or Maximum Loss; na.remove: NA Handling Routines for Time Series; NelPlo: Nelson-Plosser Macroeconomic Time Series; nino: Sea Surface Temperature (SST) Nino 3 and Nino 3.4 Indices; plotOHLC: Plot Open-High-Low-Close Bar Chart I've been trying to create an ARIMA model however, I'm not sure how to determine if the data is stationary or not. I preformed a KPSS test in R using kpss.test from package tseries and these are the results:. KPSS Level = 1.966, Truncation lag parameter = 5, p-value = 0.01 Warning message: In kpss.test(coke[,5], null = "Level") : p-value smaller than printed p .
I'm using R to calculate the KPSS to check the stationarity. The library that I'm using is tseries and the function is kpss.test I have done a simple test using cars (a default matrix on R). The. A KPSS test can be used to determine if a time series is trend stationary.. This test uses the following null and alternative hypothesis: H 0: The time series is trend stationary.; H A: The time series is not trend stationary.; If the p-value of the test is less than some significance level (e.g. α = .05) then we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that the time series is not . The KPSS (Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin) test was conducted on the lh dataset, resulting in a KPSS Level statistic of 0.29382 with a truncation lag parameter of 3. The associated p-value is 0.1. In the context of the test for level stationarity, a p-value greater than the significance level (commonly 0.05) suggests that we fail to reject .See adf.test for more details. type: the test type, only valid for method = "pp". See pp.test for more details. lag.short: a logical value, only valid for method = "pp" or "kpss". See pp.test and kpss.test for more details. output: a logical value indicating to print the results in R console. The default is TRUE.
I am using the KPSS test from the R urca package.. My result is the following: $resProp.Dwell.3 ##### # KPSS Unit Root Test # ##### Test is of type: tau with 3 lags.Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin test for stationarity. Computes the Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin (KPSS) test for the null hypothesis that x is level or trend stationary. Parameters: ¶ x array_like, 1d. The data series to test. regression str {“c”, .
KPSS test: don`t reject H0. Both imply that series is stationary. Case 3 If we can’t reject both test: data give not enough observations. Case 4 Reject unit root, reject stationarity: both hypothesis are component hypothesis – heteroskedasticity in series may make a big difference; if there is structural break it will affect inference.
1.R语言函数ur.kpss() 对于一个时间序列,例如用R自带的google股价变化数据goog(可以通过导入fpp2包之后直接使用goog这个数组变量,这里仅为示例,代指要检验的时间序列或者数组)。 . (1)比较显然地,检验的结果是用 Value of test-statistic:10.7223,来和下面最下面的4 .
Functions to estimate the number of differences required to make a given time series stationary. ndiffs estimates the number of first differences necessary.
Performs the Phillips-Perron test for the null hypothesis of a unit root of a univariate time series x (equivalently, x is a non-stationary time series). Rdocumentation. powered by. Learn R Programming. aTSA (version 3.1.2.1) Description. Usage Value,, , , Arguments.. Author. Details . KPSS Test in R, the KPSS test (Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin) is a statistical test used to determine whether a time series has a unit root or not. . To perform the KPSS test in R, we can use the “ur.kpss” function from the “urca” package. The function takes as input a time series and returns the test statistic along with its p .
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
polarimeter polarized light
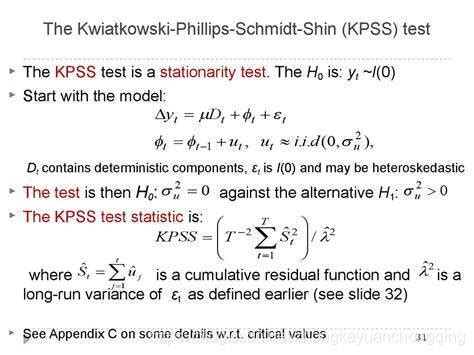
In VGAMextra: Additions and Extensions of the 'VGAM' Package. View source: R/KPSS.test.R. KPSS.test: R Documentation: KPSS tests for stationarity Description. The Kwiatkowski-Phillips-Schmidt-Shin (KPSS) test for the null hypothesis that the series x is level or trend stationary UsageDetails. To estimate sigma^2 the Newey-West estimator is used. If lshort is TRUE, then the truncation lag parameter is set to trunc(3*sqrt(n)/13), otherwise trunc(10*sqrt(n)/14) is used. The p-values are interpolated from Table 1 of Kwiatkowski et al. (1992). If the computed statistic is outside the table of critical values, then a warning message is generated.This is an interface to the unitroot tests implemented by B. Pfaff available through the R package urca which is required here. Added functions based on the urca package include: urdfTest: Augmented Dickey-Fuller test for unit roots, . KPSS Test for Unit Roots: Performs the KPSS unit root test, where the Null hypothesis is stationarity. . This post explains how to use the augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) test in R. The ADF Test is a common statistical test to determine whether a given time series is stationary or not. We explain the interpretation of ADF test results from R package by making the meaning of the alphanumeric name of test statistics clear. ADF test
kwiatkowski phillips schmidt shin test
kpss unit root test
Resultado da BDMVs are generally a copy of the files on the Blu-ray after DRM has been removed. So technically not 100% untouched, but as far as people .
kpss test in r package|how to test for stationarity